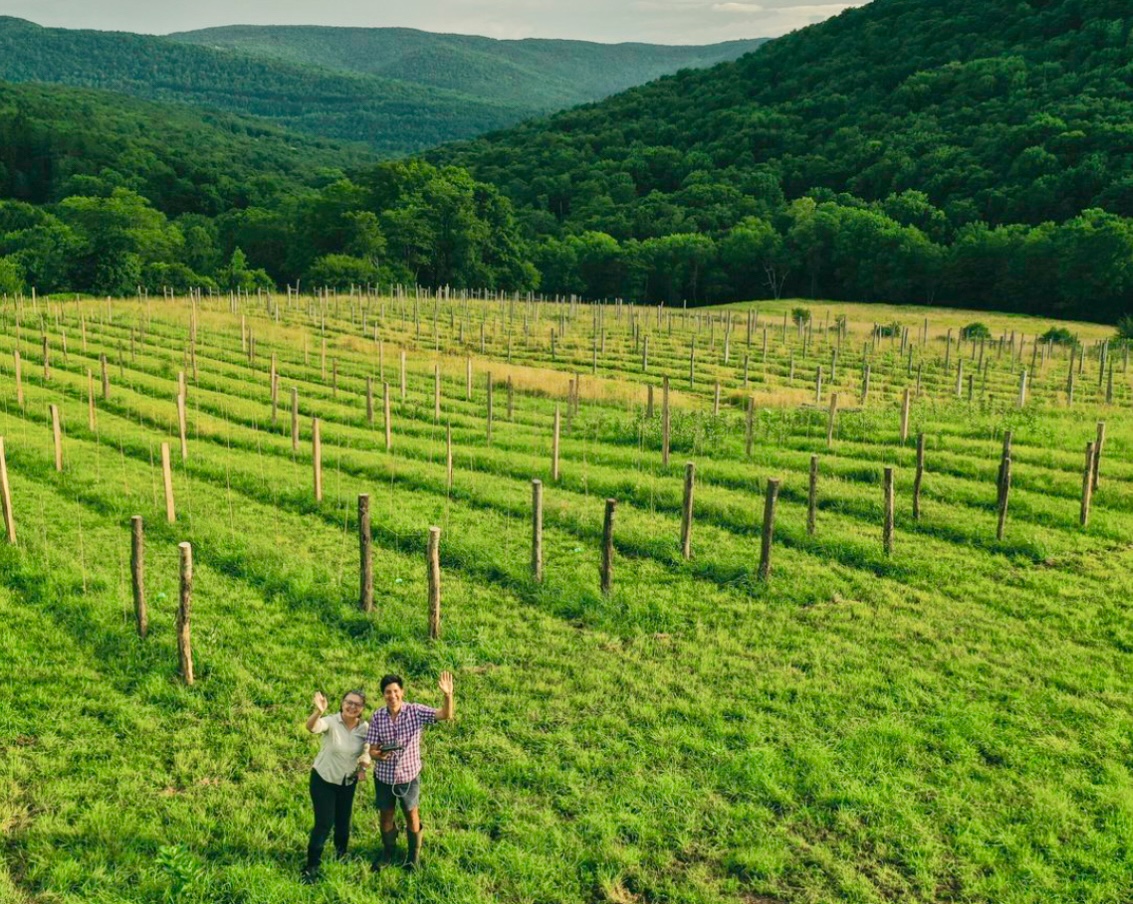
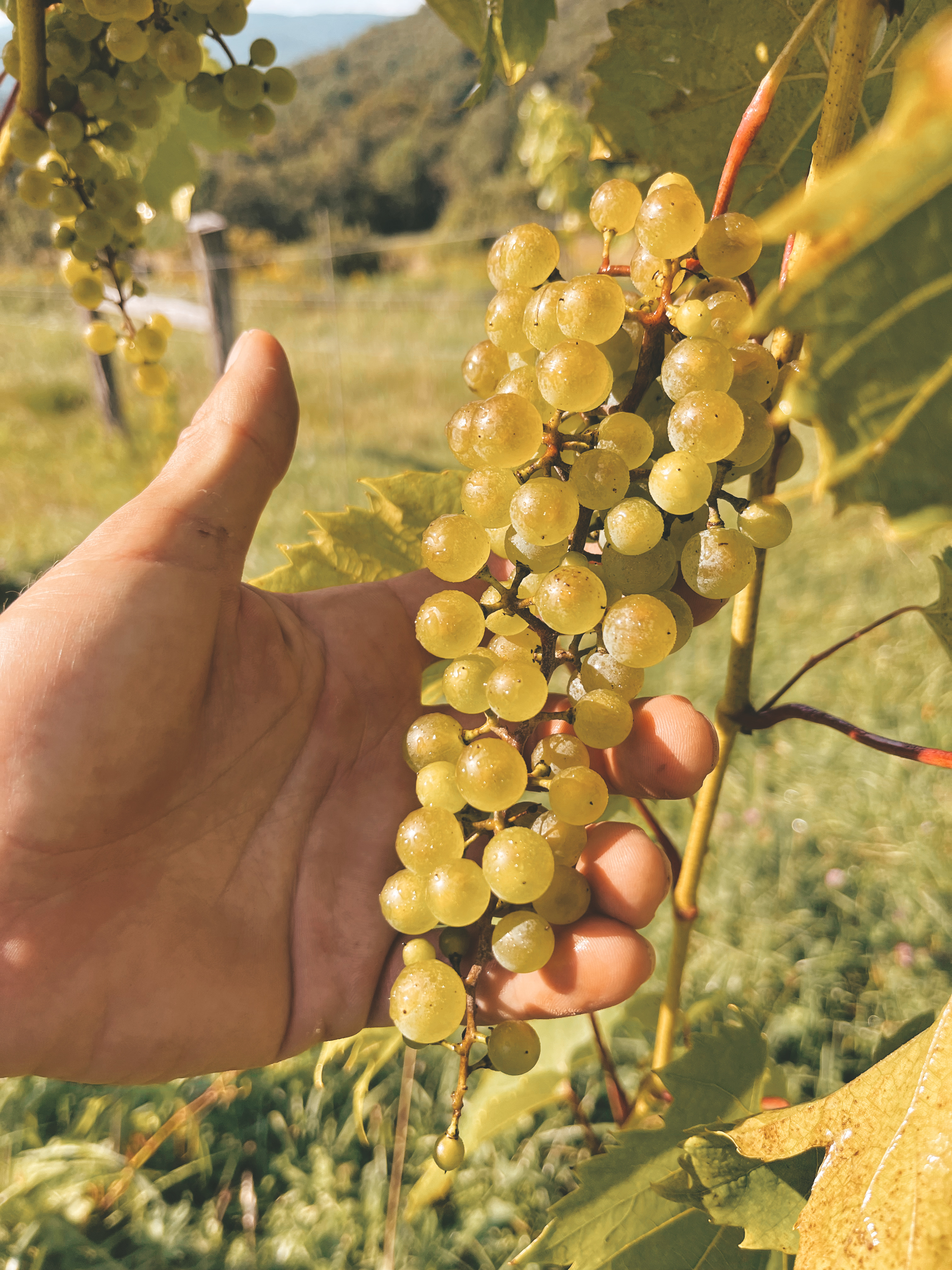
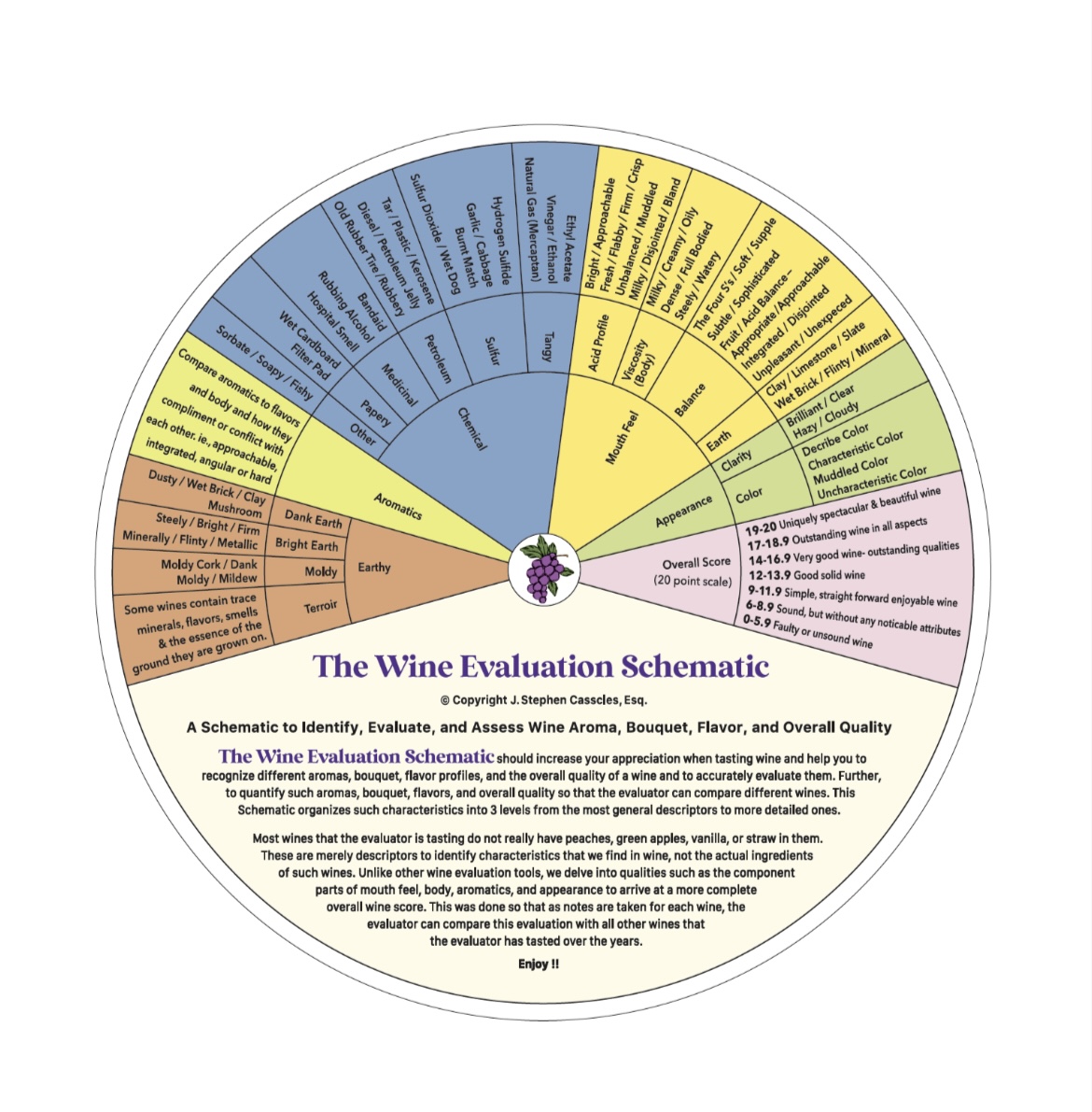
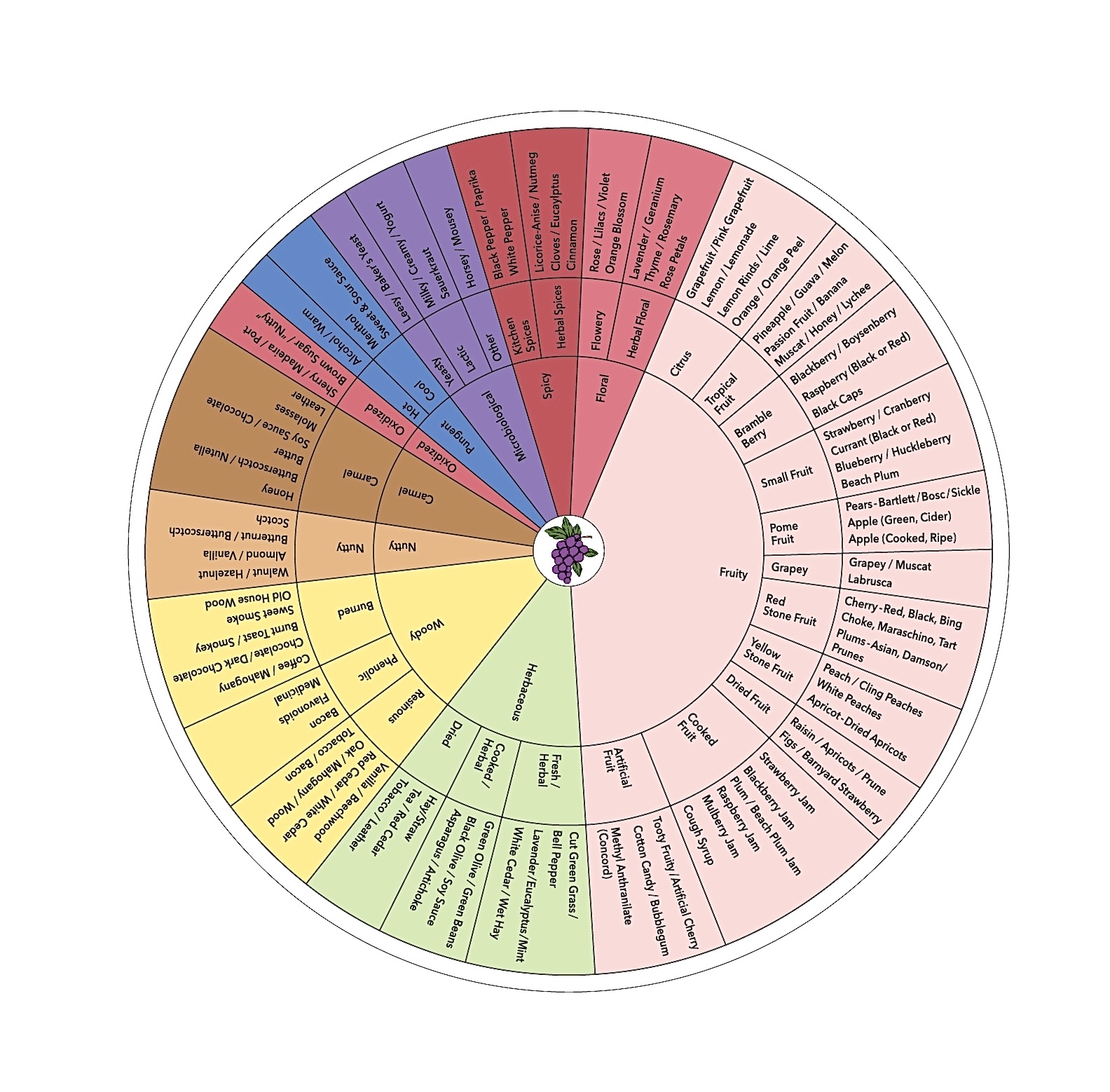
Vignerons and winemakers are adapting to the changing climate conditions in vineyards and wineries around the world. As documented in my interviews with winemakers, vineyard/winery managers, and other wine industry professionals, wine grape harvests globally occur earlier than ever before. This phenomenon is the new normal instead of the recurrent fluctuations expected over a chronicled time frame. Change in the wine world moves slowly but a small group of visionaries is leading a vanguard of growers and winemakers who are addressing the issues, not by exploring uncharted waters but by looking to the past to find answers for the future. These modern-day pioneers are resurrecting nearly forgotten grape varieties that were popular a century or more ago. They are creating exciting new wines from Heritage and Cool Climate hybrid grapes by employing unconventional winemaking methods and techniques. These strategies draw out the most favorable characteristics these grapes have to offer.
To better understand the benefits and potential that Heritage and Cool Climate grape hybrids provide, I asked J. Stephen Casscles, the leading authority in the field, for his opinions. Steve has authored extensive research on this subject, including two books, numerous articles, and scientific papers. He is also a well-known lecturer, winemaker, and owner of Cedar Cliff Vineyard, a Heritage grape vineyard in Athens, New York.
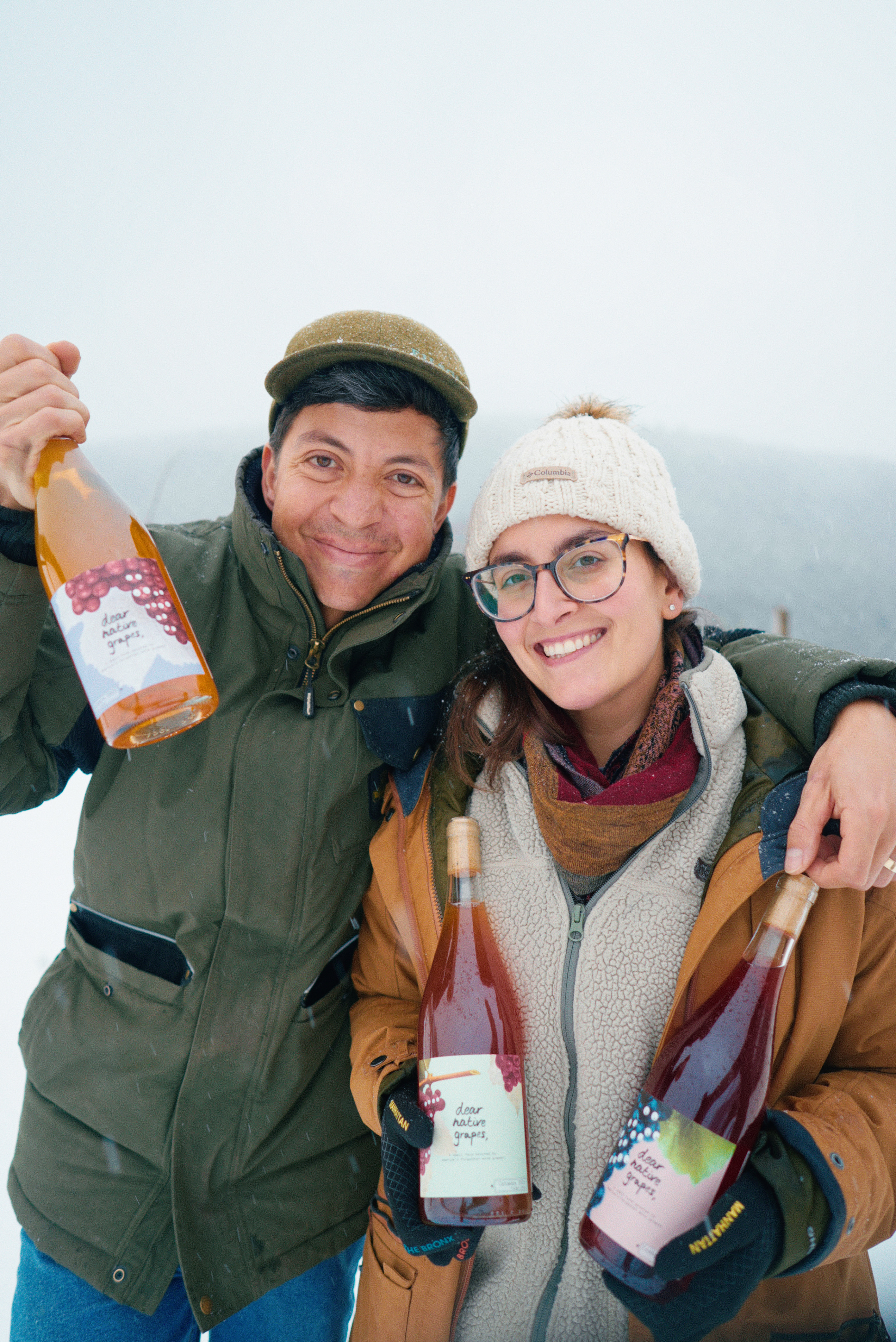
I also enlisted the help of Alfredo “Alfie” Alcántara, winemaker, Heritage grape vineyard owner, and cinematographer. Alfie is a Mexico City-raised, NYU Tisch School of the Arts grad, award-winning New York-based documentary producer, and cinematographer whose resume includes having his work screened at the Sundance Film Festival, Tribeca Film Festival, Mountainfilm in Telluride, SXSW, and CNN, just to name a few. Alfie is working closely with Steve Casscles growing and producing Heritage grape wine and co-ferments from his Dear Native Grapes Winery and Vineyard in the Catskill Mountains of New York.
The following are my interviews verbatim and in their entirety with J. Stephen Casscles and Alfredo Alcántara.
Wpawinepirate: Please share your thoughts on how growing and making wine from Heritage and interspecific grape varieties is similar to traditional procedures used with vinifera grapes, but elaborate on the differences that make your forward-looking techniques so valuable to winemaking now and especially in the future.
Casscles’s Response: “I think that growing Heritage and interspecific cool climate grape varieties are grown with the same considerations as growing vinifera. The very large difference is that while Heritage and Cool Climate hybrids are pretty forgiving when growing them in the field, that is not the case with vinifera. I find that hybrids are more productive than vinifera, are more hardy, cold-resistant, fungus disease-resistant, and are direct producers (they do not grow on root stock).
Being “direct producers”, not grown on rootstock, means that when we get our more commonly occurring late spring frosts (due to the influences of Climate Change) that inflicts heavy frost damage on the vine. The hybrids do much better. That is because since they are direct producers (not grafted) they can send shoots up from the ground THAT season and produce a crop. Also, many hybrids were bred to have a secondary crop, to have at least 1/2 a normal crop if hit by a late spring frost. With vinifera, after an especially hard late frost, there is NO secondary crop so there is no fruit crop at all AND with an esp. hard frost, the scion (top part of the vine) can be killed completely, so that all that remains is the rootstock which cannot provide any grapes. Further, Heritage and Cool Climate hybrids roll with the punches better than vinifera with what “Mother Nature” gives us …. as we have more variable growing conditions due to climate change which is bringing with it more violent weather patterns with more rain, droughts, heat, and variable hot cold temperatures, hybrids do better.
The higher resistance of hybrids to fungus and insect damage is also reflected in MUCH lower material and labor costs to grow these varieties. Vinifera grapes require much “hotter”, i.e., poisonous spray material to protect the crop than hybrids require. Also, the number of times that you need to spray vinifera with these “hot” chemicals is two to three times as many applications as the number of times needed for hybrids AND the spray materials to be used are much cheaper than that used for hybrids. This means spraying vinifera grapes 12 times a year as opposed to the 4 times needed for hybrid grapes. There is growing interest in growing grapes and other fruits either organically, semi-organically, and very much in a sustainable manner. It is nearly HOPELESS to grow vinifera organically and it has a much higher carbon footprint to grow than hybrids.
There are so many more hybrid and cool climate heritage grape varieties available to select from when setting out a vineyard. With vinifera, the “choices” are between the top 5 varieties, (In the Northeast, Chardonnay, Cabernet Sauvignon, Pinot Noir, Cabernet Franc, and Riesling), while with hybrids, there are scores of varieties that the grower can choose from to produce a sound and varied crop. This adds to diversity in the field, so that when the violent weather pattern hits the vineyard, if the grower has 10 different hybrid varieties (not just 1 or 2), the grower has a much higher probability of having a crop that produces a profit for the grower because maybe 5 of his/her varieties will still do fine with the adverse weather conditions that we are facing.
Possessing a diversity of grape varieties in each vineyard does add to the biodiversity of the plant material in the field. That means that the fungus and insect pests that can hit a vineyard can be muted because each variety has a different vulnerability to insects and various fungus diseases. However, if the grower has only 1 or 2 varieties, if a fungus or insect pest gets into the vineyard, it can wipe out the entire crop. Diversification is a strength.
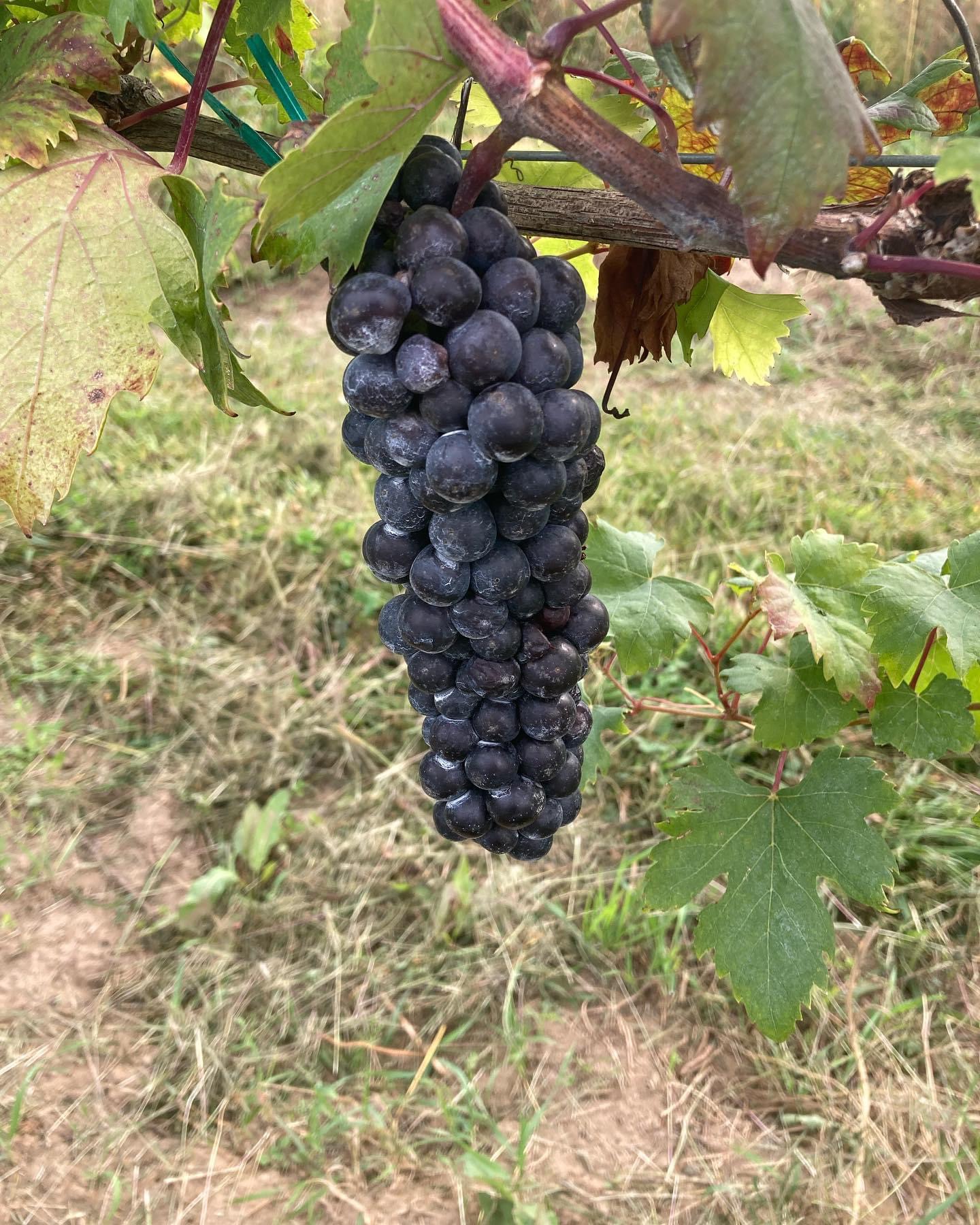
That was the first part of your question. The second is what are the benefits of making wine from these Heritage and Cool Climate hybrid grape varieties? Short answer — many many benefits. The exciting thing about making wines with Heritage and other Cool Climate varieties is the large variability in flavors, body, textures, and colors that a winemaker or co-ferment brewer has available to them to make their beverages. Varieties such as Baco Noir, Verdelet, Chelois, Bacchus, Seyval Blanc, Agawam, Empire State, Jefferson, Lindley, Leon Millot, Chambourcin, Massasoit, Burdin Noir, Le Colonel, Marion, and so many more, have a broad spectrum of flavors, aromas, colors and textures which makes it very easy to make very fun wines and co-ferments. These many different grape varieties can be used in so many different ways to make very different fun wines and co-ferments. Also, these wines tend to be fresher high acid wines that are more appealing to a new generation of consumers, with less alcohol, which is a plus for consumers both young and old.
Today’s consumers want very fruity fun wines and the Heritage and Cool Climate provide those in flavors and colors that are exciting. Some of our Rogers hybrids developed in Salem, MA in the 1850s, have colors like electric blue, hot pink, deep purple, and other fun colors.
Back to the economics and high productivity of growing Heritage and other Cool Climate grape varieties. Since they are more productive than vinifera AND can be grown with much fewer cost inputs of labor, chemicals, and other production costs, the cost of these varieties is MUCH less expensive than vinifera grapes …. which means that the cost to produce these fun and innovative wines is probably HALF of the cost of making a vinifera wine. This means that these innovative products can be provided to the consumer at a much lower cost.
It is an honor to work with both Alfie and Deanna at Dear Native Grapes to make fun wines, be it table wines, natural wines, or Pet Nats. I would rather have them speak for themselves, but I believe that we have a deep commitment to producing grapes and wines in a sustainable manner that uses far fewer pesticides and has a far lower carbon footprint. They are experimenting with making wine in many different styles for fun and for the enjoyment of our customers. I will let Alfie and Deanna talk about the grape varieties they have planted at their farm in Walton, NY, and the wines and wine styles they are striving to use to make a quality and fun product.”
Alfie’s Response: “It’s an honor to work with you, Steve! You have been our invaluable mentor throughout our journey.
“Deanna and I started ‘Dear Native Grapes’ with the goal of renewing an appreciation for America’s forgotten wine grapes. Both of us came into this with very little knowledge of winemaking or farming. But we were instantly hooked by the story of Prohibition in the 1920s and how much we lost in both the diversity of grape varieties and knowledge in wine growing. We were really driven by the thought that we could help reinvigorate something that was once valuable and productive.
While doing research for this project, we were inspired by the work of TerraVox winery in Missouri which has been diligently working with native varieties suited to the midwest, as well as Steve Casscles’ written works, especially his book ‘Grapes of the Hudson Valley And Other Cool Climate Regions of the United States and Canada’. Actually, one of the first wines we ever tasted from native varieties was made by Steve. He made it from a Hudson Valley heirloom variety called ‘Empire State’. It was so graceful and floral. We still remember its flavors and aromas. Our eyes were opened to the fact that we could create a sustainable farm and winery business in the Northeast by using the right grape varieties that could thrive in this region.
So after several years of saving up, taking business planning courses online, and volunteering at local wineries, we were finally able to afford a down payment on some farmland. We ended up in Walton, NY, in the western area of the Catskills, which is not really known for its grape growing due to the harsh climate. So our whole idea really hinged on choosing the right grape varieties that could withstand the extremes of the region.
In the spring of 2020, we planted 5 acres of grapes among three different categories:
- Contemporary cold-hardy, disease-resistant varieties like Petite Pearl, Crimson Pearl, Marquette, Frontenac, Brianna, and Itasca.
- Heirloom American varieties like Delaware, Empire State, Wine King. Some of these we propagated from cuttings from Steve’s vineyard.
- Experimental crosses are not yet available to the public. These came from modern-day grape breeders who are working to identify little-known native species that hold promise in the Northeast. Some include crosses from grape species like Vitis aestivalis, Vitis acerifolia and Vitis bicolor.
We are now four years into this project, in what seems to be a never-ending (and very sharp!) learning curve. But we’re excited to see our vines grow and we’ve already begun to identify grape varieties that have withstood the many climactic and environmental challenges we’ve experienced in the short timeline of our vineyard. An interesting variety for us has been Petite Pearl. Bred and selected in Minnesota by grape-grower Tom Plocher, this variety seems unbothered by disease pressure on our site, it’s extremely cold hardy, and most importantly, its late bud-break has managed to escape the dangerous spring frosts we’ve been having in New York. Last year we were able to produce a few gallons of wine from it, and its flavors and aromas are earthy and reminiscent of darker fruit. However, its clusters are very small, which means we’d need a much larger volume to produce a significant amount of juice.
We’ve also been surprised by the qualities of Delaware, which is not nearly as vigorous as some of the Minnesota varieties, but once it becomes established, it’s easy to prune and manage, and it produces beautiful clusters of red fruit. It’s so exciting to see some of these heirloom varieties express themselves on our site.”
Wpawinepirate: Tell us about your wine journey and vision for growing and making wine from Heritage/Cool Climate hybrid grapes.
Casscles’s Response: “How I got into grape growing is that I grew up in Marlboro, NY in the Hudson Valley, an area that has many orchards, vineyards, and berry patches. I had the fortune of living near Benmarl Vineyards and worked in the early years of Benmarl when it was established by the Miller family (Mark, Dene, Eric, and Kim). I have kept in touch with the Miller Family and my friends the Spaccarelli Family who now own Benmarl. I learned so much from working with Eric and Kim Miller about winemaking and life. I have been truly blessed and the many people who worked at Benmarl, are and continue to be family friends. From Benmarl, I learned about many of the French-American hybrids that I continue to use today. My favorites are Baco Noir, Chelois, Foch, Leon Millot (reds) Seyval Blanc, Vidal Blanc, Verdelet, and Vignoles (whites).
My vision was then and continues to be to give growers the tools and grape varieties that can be grown at a profit so they can remain in farming. Further, that will be of sufficient quality and productivity so that local wineries can make quality wines at affordable prices so that everyone at the end of a long hard day can have a glass of a quality local wine at affordable prices. Doing this can help to keep more farms in operation and quality farmland in farming and not chewed up in more housing developments. Working with, studying, identifying either Heritage grape varieties or other Cool Climate grapes, and developing methods to grow these grapes more economically is part of this effort to keep farmland in farming and to preserve those who either are in farming or wish to enter into it. It is so great to work with Alfie and Deanna because they have similar goals and work ethic to make this happen.
To advance this mission, in addition to studying such varieties, I have written, and thankfully have published, many articles to help guide those growers who want to grow hardy grape varieties that can be grown “sustainably”. In addition to Alfie and Deanna, I am so proud to work with other local grows such as Shawn Henry and his daughters Abbie and Emily of the Quimby Farm in Marlboro, NY, Jed & Jaime Radliff of Fonda, NY, Marvin Baum of the new High Tor Vineyards in Rockland County, NY, and Doug and Mirada Russell of Russell Orchards of Ipswich, MA. Together, along with Alfie and Deanna, we are forging a pathway to plant more vineyards of these Heritage varieties, propagate them to establish even more vineyards, make wine and co-ferments from these varieties, and attract new and old customers to purchase these fun beverages that can be grown sustainably and so that family farms can remain in business.“
Alfie’s Response: “We believe ‘ Dear Native Grapes’ has the potential to reimagine American wine. By expanding the varieties of grapes grown and offered to consumers, we can broaden people’s imagination. Our small winery hopes to show others what American wine could be – beautifully diverse, unabashedly unique, and wonderfully approachable.
If you think of a grape like Pinot Noir, it’s had over 600 years of human cultivation. Through slow observation and selection, the first people who farmed it started the process of shaping it to be what it is today. With American wine grapes, that process was largely halted due to historical events like Prohibition, followed by the Great Depression and WWII, and it’s just now barely restarting. We think it’s important to look at the past for answers that our ancestors have already solved and then build upon them. The Hudson Valley region in New York used to be a hotspot for horticultural innovation in the 1800s. It’s cool to think that the process of experimentation is once again alive in many other regions across the country. We might not find our American equivalent to Pinot Noir in our lifetime, but we can certainly begin to identify the great qualities in our own varieties.
We recently came across an article in the Smithsonian Magazine about Dagia Rangione, an Italian scientist who has dedicated her life to identifying and hunting down ancient varieties of fruit depicted in Renaissance paintings. Most of these heirloom varieties have long disappeared from the Italian countryside, as agriculture became industrialized over the past 200 years. The piece resonates greatly with us when she states how many of the older fruit varieties hold the keys to resilience and genetic diversity. We feel the same way about American grapes. In the article, Rangione closes with a poignant sentiment: ‘We need these old varieties to answer for the problems of the future. Without them, without roots, we are just leaves in the wind.’
At its core, Dear Native Grapes is an educational project designed to shed light on valuable grape varieties that could pave the way for more diverse, climate-resilient winemaking, energizing local economies in the process. Every year, we host visitors to share our farming methods, which are largely based on holistic management. We’re able to farm this way because our varieties actually like to grow here and have the inherent genetics to thrive in our climate. This exchange of knowledge is key to our mission, as we try to save these varieties for future generations. Our mission is not simply to make wine from these varieties, but to offer others a viable path for doing the same.”
When growing a vineyard of wine grapes, as with any of life’s endeavors, the ready availability of options always enhances the probability of success. In the agricultural community, the ability to foresee potential problems is a skill set only honed to a fine edge with experience. Planting a crop that can survive and prosper under many adverse conditions is essential to any project’s long-term sustainability. Diversifying the varieties of grape vines planted in a vineyard has proven beneficial and has justified the old adage “Diversity is a Strength”.
I sincerely appreciate Steve Casscles and Alfie Alcántara for taking time from their busy schedules to share this invaluable information and their unique perspectives on this timely subject. If you have any questions feel free to contact them
(Steve) cassclesjs@yahoo.com
(Alfie) alfie.alcantara@gmail.com
http://dearnativegrapes.com
Photo Credit: J. Stephen Casscles, Alfredo “Alfie” Alcantara, and Dear Native Grapes